Sleep - Insomnia
Amitriptyline
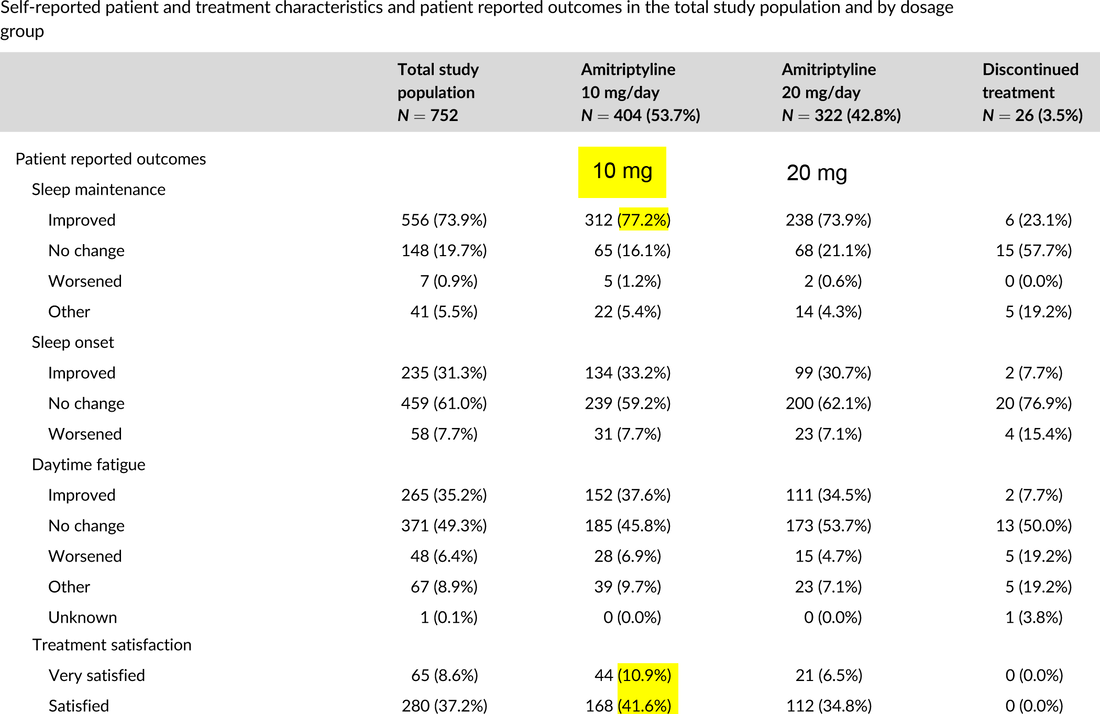
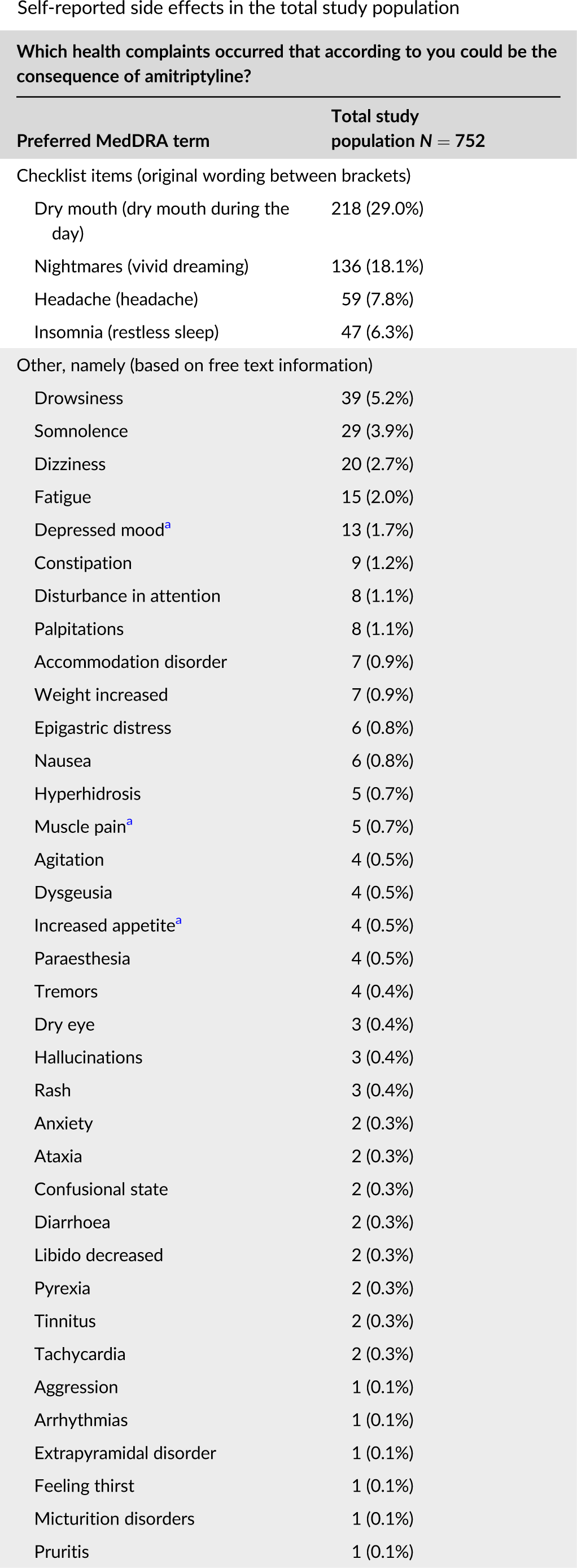
Off-label low dose amitriptyline for insomnia disorder: Patient-reported outcomes.
Bakker MH, Hugtenburg JG, Smits MG, van der Horst HE, Slottje P. Off-label low dose amitriptyline for insomnia disorder: Patient-reported outcomes. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2022 Oct 30. available here.
Bakker MH, Hugtenburg JG, Smits MG, van der Horst HE, Slottje P. Off-label low dose amitriptyline for insomnia disorder: Patient-reported outcomes. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2022 Oct 30. available here.
NOTE: 10 mg generally superior to 20 mg (which includes higher doses).
Doxepin (Low-Dose)
The tricyclic antidepressant doxepin (Silenor) is the only antidepressant approved by the FDA for the treatment of sleep-maintenance insomnia. Its affinity for H1 histamine receptors is thought to be largely responsible for its sedating effect. In doses much lower than those used to treat depression (3-6 mg vs 150-300 mg), it is claimed to have a hypnotic effect without causing anticholinergic and other typical tricyclic adverse effects. Some clinical studies have demonstrated effcacy both in healthy volunteers (51 minutes more total sleep time) and in elderly patients with chronic insomnia.Doxepin is contraindicatedfor use with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) or within two weeks of stopping one.
Other antidepressants commonly used for sleep: trazodone (Desyrel, and generics), mirtazapine (Remeron, and generics), and amitriptyline (Elavil, and generics).
Gabapentin/Pregabalin
May have a beneficial effect on sleep. Increase slow-wave sleep and sleep efficiency.
Suvorexant (Belsomra)
Signaling of orexin neuropeptides sustains wakefulness. Clinical studies have shown that patients treated with the drug fall asleep 5-10 minutes sooner and stay asleep 15-25 minutes longer than those given placebo. Adverse Effects – Suvorexant is classified as a schedule IV controlled substance. Its most serious side effect, related to its long half-life, is next-day somnolence, which may impair performance skills such as driving. Cataplexy-like symptoms such as leg weakness
occurred in a few patients in clinical trials. Suvorexant should be administered with caution to patients with compromised respiratory function; it appears to be safe in patients with mild to moderate COPD. Drug Interactions – Suvorexant is a substrate of CYP3A4 and should not be administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as clarithromycin. In patients
taking moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as fluconazole (Diflucan, and generics), verapamil (Calan, and others), or grapefruit juice, the recommended dose of suvorexant is 5 mg, which can be increased to 10 mg if needed. The efficacy of suvorexant may be reduced in patients concomitantly taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer such as carbamazepine. Suvorexant is a P-glycoprotein inhibitor; concomitant administration with digoxin increased digoxin serum concentrations. Concurrent use of alcohol or other CNS depressants increases the risk of CNS depression. Onset: 30 min. Duration: intermediate. Dose: 10-20 mg. Dose in elderly: 10-20 mg.
Ramelteon (Rozerem)
Clinical studies have shown statistically significant but clinically modest improvements in sleep parameters. Adverse Effects – Common adverse effects of ramelteon include dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and headache. Increased serum prolactin and decreased serum testosterone concentrations have been reported. Unlike benzodiazepine receptor agonists and benzodiazepines, ramelteon has no potential for abuse and is not classified as a controlled substance. Drug Interactions – Ramelteon is metabolized by CYP1A2 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and 3A4. Concurrent administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluvoxamine (Luvox, and others), which is a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor, markedly increases serum concentrations of ramelteon; they should not be taken together. Other CYP1A2 inhibitors, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro, and others), could have a similar effect. Drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 or 2C9 could also increase ramelteon serum concentrations and the risk of toxicity. Rifampin, a potent inducer of various CYP isozymes, decreases ramelteon serum concentrations by 80% and presumably would decrease its hypnotic effect. nset of action: 15-30 min. Duration: short, Usual hypnotic dose: 8 mg.
The tricyclic antidepressant doxepin (Silenor) is the only antidepressant approved by the FDA for the treatment of sleep-maintenance insomnia. Its affinity for H1 histamine receptors is thought to be largely responsible for its sedating effect. In doses much lower than those used to treat depression (3-6 mg vs 150-300 mg), it is claimed to have a hypnotic effect without causing anticholinergic and other typical tricyclic adverse effects. Some clinical studies have demonstrated effcacy both in healthy volunteers (51 minutes more total sleep time) and in elderly patients with chronic insomnia.Doxepin is contraindicatedfor use with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) or within two weeks of stopping one.
Other antidepressants commonly used for sleep: trazodone (Desyrel, and generics), mirtazapine (Remeron, and generics), and amitriptyline (Elavil, and generics).
Gabapentin/Pregabalin
May have a beneficial effect on sleep. Increase slow-wave sleep and sleep efficiency.
Suvorexant (Belsomra)
Signaling of orexin neuropeptides sustains wakefulness. Clinical studies have shown that patients treated with the drug fall asleep 5-10 minutes sooner and stay asleep 15-25 minutes longer than those given placebo. Adverse Effects – Suvorexant is classified as a schedule IV controlled substance. Its most serious side effect, related to its long half-life, is next-day somnolence, which may impair performance skills such as driving. Cataplexy-like symptoms such as leg weakness
occurred in a few patients in clinical trials. Suvorexant should be administered with caution to patients with compromised respiratory function; it appears to be safe in patients with mild to moderate COPD. Drug Interactions – Suvorexant is a substrate of CYP3A4 and should not be administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as clarithromycin. In patients
taking moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors, such as fluconazole (Diflucan, and generics), verapamil (Calan, and others), or grapefruit juice, the recommended dose of suvorexant is 5 mg, which can be increased to 10 mg if needed. The efficacy of suvorexant may be reduced in patients concomitantly taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer such as carbamazepine. Suvorexant is a P-glycoprotein inhibitor; concomitant administration with digoxin increased digoxin serum concentrations. Concurrent use of alcohol or other CNS depressants increases the risk of CNS depression. Onset: 30 min. Duration: intermediate. Dose: 10-20 mg. Dose in elderly: 10-20 mg.
Ramelteon (Rozerem)
Clinical studies have shown statistically significant but clinically modest improvements in sleep parameters. Adverse Effects – Common adverse effects of ramelteon include dizziness, nausea, fatigue, and headache. Increased serum prolactin and decreased serum testosterone concentrations have been reported. Unlike benzodiazepine receptor agonists and benzodiazepines, ramelteon has no potential for abuse and is not classified as a controlled substance. Drug Interactions – Ramelteon is metabolized by CYP1A2 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9 and 3A4. Concurrent administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) fluvoxamine (Luvox, and others), which is a strong CYP1A2 inhibitor, markedly increases serum concentrations of ramelteon; they should not be taken together. Other CYP1A2 inhibitors, such as ciprofloxacin (Cipro, and others), could have a similar effect. Drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 or 2C9 could also increase ramelteon serum concentrations and the risk of toxicity. Rifampin, a potent inducer of various CYP isozymes, decreases ramelteon serum concentrations by 80% and presumably would decrease its hypnotic effect. nset of action: 15-30 min. Duration: short, Usual hypnotic dose: 8 mg.
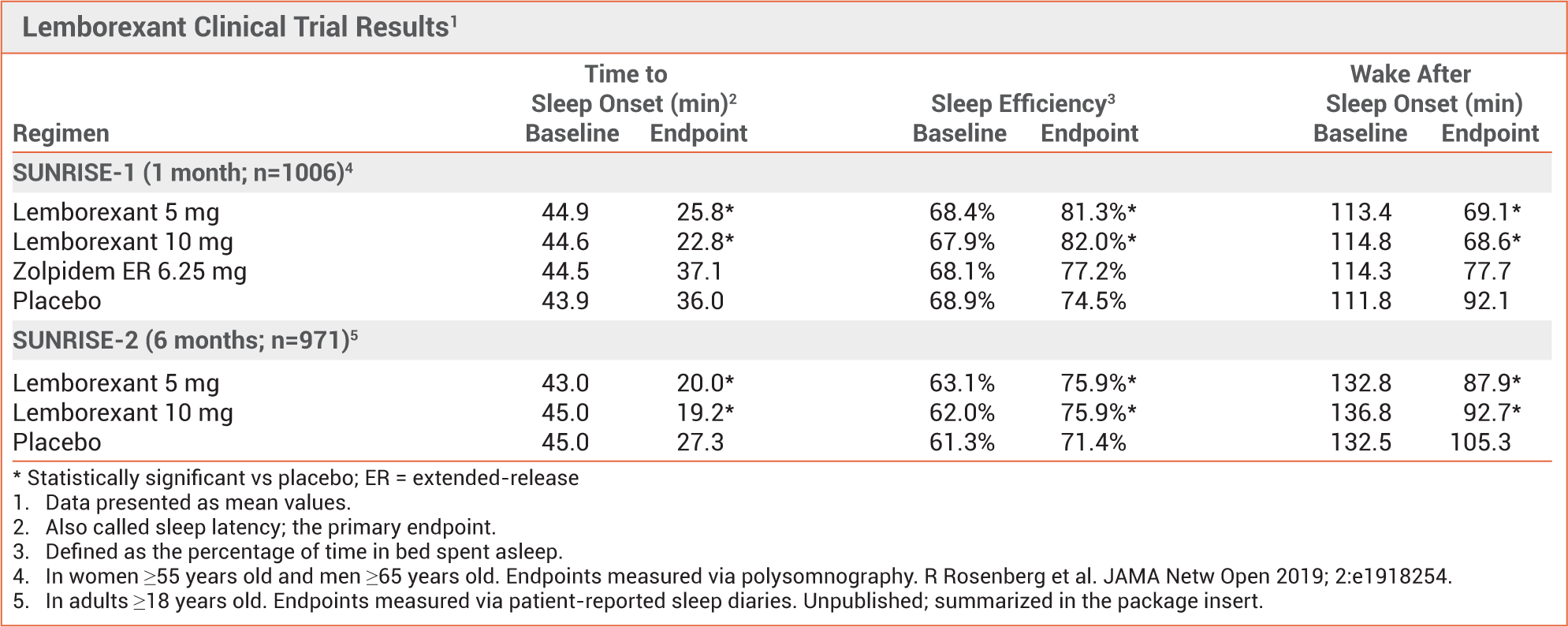
Lemborexant (Dayvigo) vs. Zolpidem
▶ Lemborexand is approved for treatment of sleep onset and/or sleep-maintenance insomnia in adults.
The second orexin receptor antagonist approved by the FDA for treatment of insomnia; suvorexant (Belsomra) was the first.
▶ Competitively inhibits the neuropeptides orexin A and B, which promote wakefulness.
▶ Significantly improved sleep latency and sleep efficiency compared to placebo in 2 randomized trials.
▶ In safety studies, lemborexant 5 mg was not significantly different from placebo in next-day postural stability, memory,
attention, and driving ability.
▶ Classified as a schedule IV controlled substance
ADVERSE EFFECTS — Somnolence/fatigue, headache, and nightmares/abnormal dreams occurred more frequently with lemborexant than with placebo in clinical trials. Symptoms similar to mild cataplexy, including leg weakness lasting up to a few minutes, can occur. Sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations, complex sleep behavior (e.g., walking, driving, or preparing and eating food while not fully awake), worsening depression, and suicidal ideation/behavior have been reported. Lemborexant has not been associated with rebound insomnia or withdrawal effects after drug discontinuation, but CNS depression can persist for several days. Like suvorexant, lemborexant is classified as a schedule IV controlled substance.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION — The recommended dosage of lemborexant is 5 mg once per night, taken immediately before bedtime and ≥7 hours before planned awakening time. The nightly dose can be increased to a maximum of 10 mg, depending on response and tolerability. Taking the drug with or soon after a meal may delay the time to sleep onset.
The second orexin receptor antagonist approved by the FDA for treatment of insomnia; suvorexant (Belsomra) was the first.
▶ Competitively inhibits the neuropeptides orexin A and B, which promote wakefulness.
▶ Significantly improved sleep latency and sleep efficiency compared to placebo in 2 randomized trials.
▶ In safety studies, lemborexant 5 mg was not significantly different from placebo in next-day postural stability, memory,
attention, and driving ability.
▶ Classified as a schedule IV controlled substance
ADVERSE EFFECTS — Somnolence/fatigue, headache, and nightmares/abnormal dreams occurred more frequently with lemborexant than with placebo in clinical trials. Symptoms similar to mild cataplexy, including leg weakness lasting up to a few minutes, can occur. Sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations, complex sleep behavior (e.g., walking, driving, or preparing and eating food while not fully awake), worsening depression, and suicidal ideation/behavior have been reported. Lemborexant has not been associated with rebound insomnia or withdrawal effects after drug discontinuation, but CNS depression can persist for several days. Like suvorexant, lemborexant is classified as a schedule IV controlled substance.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION — The recommended dosage of lemborexant is 5 mg once per night, taken immediately before bedtime and ≥7 hours before planned awakening time. The nightly dose can be increased to a maximum of 10 mg, depending on response and tolerability. Taking the drug with or soon after a meal may delay the time to sleep onset.